Joint pain is a widespread concern, touching people across all age groups. Whether it stems from an injury, arthritis, or the simple grind of daily life, the pain can be crippling. But before you turn to prescription medications, why not explore some natural home remedies that could ease your discomfort?
These remedies are not only natural but seamlessly fit into your daily routine. In this article, we’ll delve into the top home remedies for joint pain relief, aiming to help you return to your daily activities with greater ease and less pain.
Introduction to Joint Pain
Joint pain is a universal complaint that impacts millions of people worldwide. From athletes to the elderly, the discomfort can range from a minor annoyance to a severe hindrance. Joint pain can strike abruptly or gradually worsen. Although acute injuries like torn or sprained ligaments can cause it, chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis are more frequent culprits.
Joint pain is common and can affect anyone. It often happens in the knees due to their important role in movement. Pain can be mild or severe and caused by injury, wear and tear, or conditions like arthritis. It can make everyday activities difficult. Luckily, many cases can be treated with home care, lifestyle changes, or medical help. Early attention helps prevent worsening pain. Knowing what causes your pain is the first step to feeling better.
Understanding the Causes of Joint Pain
Joint pain can arise from a variety of causes, and understanding these causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. The knee is a complex masterpiece of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles working in perfect harmony to enable movement. Any disruption to this intricate system can trigger knee pain. Understanding the underlying cause of joint pain is crucial in determining the appropriate remedies. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Injuries: Such as fractures, torn ligaments, or meniscus tears.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.
- Mechanical Problems: Dislocated kneecap, loose body, or hip or foot pain.
- Infections: Joint infections can cause significant discomfort and require immediate attention.
Injuries
1. Ligament Injuries
The knee is stabilized by several key ligaments, including the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), and the medial and lateral collateral ligaments (MCL and LCL). Injuries to these ligaments, such as tears or sprains, often occur during sports or activities that involve sudden changes in direction, jumping, or high-impact landings. An ACL tear, for instance, is a common injury among athletes and can cause significant knee instability and pain.
2. Meniscus Tears
The menisci are two pieces of cartilage that act as shock absorbers between your thighbone and shinbone. A meniscus tear can occur from twisting or turning your knee quickly while your foot is planted, often during sports. This type of injury can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee.
3. Fractures
Fractures of the knee bones, such as the patella (kneecap), can occur due to trauma, like a fall or car accident. These injuries are often extremely painful and require immediate medical attention.
4. Tendonitis
Tendonitis, or inflammation of the tendons, is common in athletes who engage in repetitive activities like running, jumping, or cycling. The patellar tendon, which connects the quadriceps muscles to the shinbone, is particularly prone to this condition, often referred to as “jumper’s knee.”
Arthritis
1. Osteoarthritis
The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. This leads to pain, swelling, and stiffness in the knee. Osteoarthritis is often associated with aging, but it can also be influenced by factors like obesity, previous injuries, and genetics.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis, which is primarily a degenerative condition, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This causes inflammation, pain, and eventually, joint damage.
3. Gout
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joint, leading to sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling. The knee is one of the joints that can be affected by gout.
4. Septic Arthritis
This is a less common but serious condition where an infection invades the joint, causing severe pain, swelling, redness, and fever. Septic arthritis requires prompt medical treatment to prevent joint damage.
Mechanical Problems
1) Dislocated Kneecap
This is also known as patellar dislocation. This occurs when the patella slides out of its normal position, usually to the outside of the knee. It can cause intense pain and swelling and may require medical intervention to realign the kneecap.
2) Loose Bodies
Sometimes, injury or degeneration can cause fragments of bone or cartilage to break off and float within the joint space. These loose bodies can interfere with knee movement, causing pain and a sensation of the knee “locking” or “catching.”
3) Iliotibial Band Syndrome
The iliotibial (IT) band is a thick band of tissue that runs from the outside of your hip to the outside of your knee. Overuse or tightness in the IT band can cause pain on the outer side of the knee, a condition commonly seen in runners and cyclists.
Infections
1) Bursitis
The bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint. Inflammation of these sacs, known as bursitis, can occur due to overuse, trauma, or infection, leading to pain and swelling.
2) Tendinitis
Infection of the tendons around the knee, although rare, can also cause significant pain and require immediate treatment.
Other Causes
Overuse Injuries
Repeated stress on the knee from activities like running, cycling, or squatting can lead to overuse injuries. These injuries can cause pain and inflammation in various parts of the knee, such as the tendons and bursae.
Biomechanical Issues
Leg alignment issues, such as knock-knees or bowlegs, can excessively strain the knee joint, eventually causing pain. Additionally, issues with the hips, feet, or lower back can alter the way you walk, further contributing to knee pain.
Obesity
Excess body weight increases the load on your knee joints, even during normal activities like walking or going up and down stairs. Over time, this additional stress can lead to the breakdown of joint tissues and the development of conditions like osteoarthritis.
Understanding the specific cause of your knee pain is essential in determining the most effective treatment approach. While some causes, like minor injuries or overuse, can often be managed with home remedies and rest, others may require medical intervention. By addressing the root cause of your knee pain, you can take the necessary steps to alleviate discomfort and prevent future issues.
Why Home Remedies?
When it comes to managing knee pain, the first thought for many might be to reach for over-the-counter painkillers or even seek prescription medications. However, there are compelling reasons to consider home remedies as a first line of defense. These natural approaches not only provide effective relief but also offer a holistic way to address the root causes of pain without the potential side effects associated with pharmaceutical treatments.
Safety and Fewer Side Effects
One of the main advantages of home remedies is their safety profile. Many conventional medications, particularly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, liver or kidney damage, and dependency when used long-term. In contrast, home remedies like herbal supplements, gentle exercises, and dietary changes typically pose minimal risks when used correctly. They allow you to manage your pain without worrying about the potential for adverse effects.
Accessibility and Cost-Effectiveness
Home remedies are often more accessible and cost-effective than conventional treatments. Many of the ingredients or tools needed for home remedies, such as ice packs, essential oils, or certain foods, are readily available at home or can be purchased inexpensively. This accessibility makes it easier to implement and maintain these remedies as part of your daily routine, especially for those who may not have immediate access to healthcare services or who want to reduce medical expenses.
Holistic Approach to Pain Management
Home remedies often take a holistic approach to pain management, addressing not just the symptoms but also the underlying causes of knee pain. For example, weight management through diet and exercise not only reduces the load on your knee joints but also improves overall health. Similarly, practices like yoga and meditation address both physical and mental aspects of pain, helping to reduce stress and improve coping mechanisms. This comprehensive approach can lead to more sustainable pain relief and better long-term outcomes.
Empowerment and Self-Care
Using home remedies encourages a proactive approach to health and well-being. By taking control of your pain management through natural means, you become more attuned to your body’s needs and responses. This empowerment can lead to a greater sense of well-being and a more positive outlook on managing chronic conditions. Additionally, the routine of self-care practices, such as applying hot or cold therapy or performing gentle stretches, can become a comforting and therapeutic ritual.
Complementary to Conventional Treatments
Home remedies can be used alongside conventional treatments to enhance their effectiveness. For instance, applying ice packs or using compression can complement physical therapy exercises prescribed by your doctor. Herbal supplements like turmeric or ginger can be taken in conjunction with NSAIDs to reduce inflammation naturally, potentially allowing you to use lower doses of medication. This integrative approach can provide comprehensive relief and improve your overall treatment plan.
Personalized Care
Home remedies offer a personalized approach to care, allowing you to tailor your treatment to your specific needs and preferences. Everyone’s experience of knee pain is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. With home remedies, you have the flexibility to experiment with different methods and find the combination that best suits your body and lifestyle. This individualized care can lead to more effective and satisfying pain management.
Finally, home remedies offer a natural, accessible, and holistic way to manage knee pain. They provide a safe alternative or complement to conventional treatments, empowering you to take control of your health and well-being. By incorporating these remedies into your daily routine, you can reduce discomfort, improve joint function, and enhance your overall quality of life.

Home Remedies For Joint Pain Relief
Joint pain can be a debilitating condition that affects people of all ages. While medical intervention is often necessary for severe cases, many individuals find relief through home remedies. These natural approaches can help manage discomfort, reduce inflammation, and improve overall joint health.
1. R.I.C.E Method
The R.I.C.E method is one of the most effective home remedies for knee pain, particularly after an injury. It is a time-tested approach to managing acute knee injuries and pain, especially in the initial stages following an injury.
The R.I.C.E. method is also a cornerstone of first-aid treatment for knee injuries. Its effectiveness in reducing pain, swelling, and promoting healing makes it a go-to strategy for anyone dealing with knee pain.
This method is widely recommended by healthcare professionals and is effective in reducing pain, minimizing swelling, and promoting faster recovery.
It stands for:
- Rest: Give your knee a break and avoid putting too much weight on it.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Compression: Use a knee brace or elastic bandage to provide support.
- Elevation: Keep your knee elevated to reduce swelling.
This method is a go-to for many athletes and is highly recommended in the first 48 hours following an injury.
Here’s a deeper look into each component of the R.I.C.E. method:
A] Rest

Rest is the first and most crucial step in the R.I.C.E. method. When you experience knee pain, particularly after an injury, it’s essential to give your knee the time it needs to heal. Resting the affected area helps prevent further injury and allows the body’s natural healing processes to take place.
Why Is Rest Important?
Continuing to use the injured knee can exacerbate the damage, leading to increased pain, swelling, and a longer recovery time. Resting might involve avoiding activities that put strain on the knee, such as walking, running, or lifting heavy objects. In some cases, using crutches or a knee brace might be necessary to keep weight off the knee and provide additional support during the healing process.
How Long Should You Rest?
The duration of rest depends on the severity of the injury. For minor injuries, a few days of rest may be sufficient. However, more severe injuries might require several weeks or even months of limited activity. It’s important to listen to your body and avoid rushing back into activities before your knee is fully healed.
B] Ice
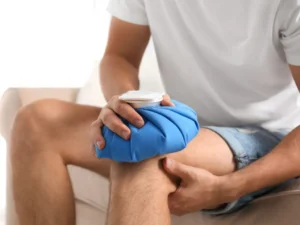
Applying ice to the injured knee is a simple yet highly effective way to reduce pain and swelling. Ice therapy, also known as cryotherapy, works by constricting blood vessels, which reduces blood flow to the affected area and minimizes inflammation.
How To Apply Ice?
To apply ice, wrap an ice pack or a bag of frozen peas in a thin towel and place it on the affected knee. Avoid placing ice directly on the skin, as this can cause frostbite. Apply the ice for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, especially during the first 48 hours following the injury.
Why Is Ice Important?
In addition to reducing swelling, ice helps numb the area, providing temporary pain relief. This can be particularly beneficial immediately after the injury, when pain and swelling are at their peak. Regular ice application can also help prevent further tissue damage.
C] Compression
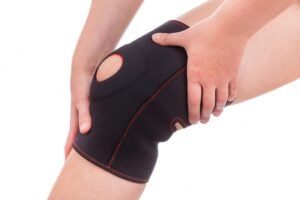
Compression involves applying gentle pressure to the injured knee to help reduce swelling and provide support. This is typically done using an elastic bandage or a knee brace.
How To Apply Compression?
When using an elastic bandage, start wrapping at the lower part of the knee and work your way upward, overlapping the bandage with each pass. The bandage should be snug but not so tight that it restricts blood flow or causes additional pain. If your knee starts to feel numb, cold, or tingly, loosen the bandage immediately. A knee brace can also provide compression while allowing for some movement.
Why Is Compression Important?
Compression helps control swelling by preventing the accumulation of fluids around the knee joint. It also offers support to the injured area, which can be particularly helpful if the injury has caused instability in the knee. By reducing swelling and stabilizing the joint, compression aids in the overall healing process.
D] Elevation

Elevation is the final component of the R.I.C.E. method and involves keeping the injured knee raised above the level of your heart. This position helps reduce swelling by encouraging fluid drainage away from the injured area.
How To Elevate Your Knee?
To properly elevate your knee, lie down and prop your leg up on pillows or a cushioned surface. Ensure that your knee is comfortably supported and elevated higher than your heart. This position can be maintained while resting or sleeping.
Why Is Elevation Important?
Elevation works in conjunction with the other steps of the R.I.C.E. method to reduce swelling and pain. By using gravity to your advantage, elevation helps decrease fluid accumulation in the knee, which can lead to a quicker reduction in swelling and discomfort. It also helps improve circulation, which is vital for delivering nutrients and oxygen to the injured tissues, promoting faster healing.
Combining The R.I.C.E. Method
The beauty of the R.I.C.E. method lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. By combining rest, ice, compression, and elevation, you create an environment that fosters healing and reduces the risk of further injury. While each component of the R.I.C.E. method plays a crucial role individually, their combined effect is what makes this approach so powerful.
When To Use The R.I.C.E. Method
The R.I.C.E. method is particularly useful in the first 24 to 48 hours following an injury. It’s most effective for managing acute injuries, such as sprains, strains, and ligament tears, that involve inflammation and swelling. However, it can also be beneficial for flare-ups of chronic conditions like arthritis, where inflammation and pain are present.
If you don’t see improvement in your knee pain after a few days of using the R.I.C.E. method, or if the pain and swelling worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent or severe pain may indicate a more serious issue that requires medical attention, such as a fracture, severe ligament tear, or infection.
2. Gentle Exercises and Stretches
Gentle exercises and stretches are essential components of a comprehensive approach to managing knee pain. They help build strength, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability, all of which contribute to overall knee health. Incorporating gentle exercises and stretches into your routine can play a crucial role in managing knee pain and improving overall knee health.
While it may seem counterintuitive to exercise a painful joint, the right kind of movement can actually aid in reducing pain, strengthening the muscles around the knee, and enhancing flexibility. Let’s explore some effective exercises and stretches designed specifically for knee pain relief.
Benefits of Gentle Exercises
a) Strengthening Muscles
Strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, provides better support for the joint. Stronger muscles help absorb the impact on the knee, reducing strain and preventing further injury.
b) Improving Flexibility
Regular stretching helps maintain and improve the flexibility of the knee joint and surrounding muscles. This flexibility can alleviate stiffness and enhance your range of motion, making daily activities easier and less painful.
c) Enhancing Joint Stability
Exercises that focus on balance and stability help stabilize the knee joint, reducing the risk of future injuries. Improved joint stability can also enhance overall mobility and functional strength.
d) Reducing Inflammation
Gentle movement stimulates blood flow, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Increased circulation delivers essential nutrients to the knee joint and helps flush out metabolic waste products that can contribute to pain and swelling.
Recommended Exercises
A. Quadriceps Sets

How to do it: Sit or lie down with your legs straight. Tighten the muscles at the front of your thigh (quadriceps) and press the back of your knee down toward the floor. Hold for 5-10 seconds, then relax.
Repetitions: Perform 10-15 repetitions, 2-3 times a day.
Benefits: This exercise strengthens the quadriceps, which helps support the knee joint and improve knee stability.
B. Straight Leg Raises

How to do it: Lie on your back with one knee bent and the other leg straight. Tighten your thigh muscles and slowly lift the straight leg to the height of the bent knee. Hold for a few seconds, then slowly lower it back down.
Repetitions: Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg, 2-3 times a day.
Benefits: Straight leg raises strengthen the quadriceps and hip flexors without putting additional stress on the knee joint.
C. Hamstring Curls

How to do it: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and hold onto a chair or wall for balance. Bend one knee and lift your heel toward your buttocks. Hold for a few seconds, then lower your foot back down.
Repetitions: Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg, 2-3 times a day.
Benefits: This exercise targets the hamstrings, which are crucial for knee support and movement.
D. Calf Raises

How to do it: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and slowly rise onto your toes, then lower back down. You can hold onto a chair or wall for balance.
Repetitions: Perform 10-15 repetitions, 2-3 times a day.
Benefits: Calf raises strengthen the calf muscles and improve overall leg stability.
E. Wall Slides
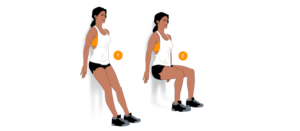
How to do it: Stand with your back against a wall and slide down into a seated position, keeping your knees aligned with your toes. Hold for a few seconds, then slowly slide back up.
Repetitions: Perform 10-15 repetitions, 2-3 times a day.
Benefits: Wall slides help strengthen the quadriceps and improve knee range of motion while providing a low-impact workout.
Recommended Stretches
A) Hamstring Stretch

How to do it: Sit on the floor with one leg extended straight and the other bent with the foot against the inner thigh of the extended leg. Reach toward the toes of the extended leg and hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds.
Repetitions: Repeat 2-3 times on each leg.
Benefits: This stretch improves flexibility in the hamstrings, which can help alleviate knee discomfort.
B) Quadriceps Stretch

How to do it: Stand and hold onto a chair or wall for balance. Bend one knee and grab your ankle with your hand, gently pulling it toward your buttocks. Hold for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs.
Repetitions: Repeat 2-3 times on each leg.
Benefits: Stretching the quadriceps helps reduce tension in the front of the thigh and improves knee mobility.
C. Calf Stretch

How to do it: Stand facing a wall with one foot forward and the other foot extended back. Keep the back leg straight and press the heel into the floor while leaning forward. Hold for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs.
Repetitions: Repeat 2-3 times on each leg.
Benefits: This stretch targets the calf muscles and helps improve flexibility and reduce strain on the knee.
D. Iliotibial (IT) Band Stretch

How to do it: Stand with one leg crossed over the other and gently lean to the side of the back leg, reaching your arm overhead. Hold for 15-30 seconds, then switch sides.
Repetitions: Repeat 2-3 times on each side.
Benefits: Stretching the IT band can alleviate pain on the outer side of the knee and improve overall knee function.
Tips for Safe Exercise
a. Warm Up
Always warm up before starting exercises with light activities like walking or gentle stretching to prepare your muscles and joints.
b. Listen to Your Body
Start slowly and avoid exercises that cause increased pain or discomfort. Modify or skip exercises if needed.
c. Consistency is Key
Incorporate these exercises and stretches into your daily routine for the best results. Consistent effort will yield better long-term benefits.
d. Consult a Professional
If you have any underlying health conditions or severe knee pain, consult a physical therapist or healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program.
3. Herbal Remedies and Natural Supplements
Many herbs and natural supplements are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. For instance, turmeric contains curcumin, which has been shown to reduce inflammation. Ginger, boswellia, and willow bark are other herbs that can be used to manage knee pain naturally. These can be taken as supplements or incorporated into your diet.
4. Essential Oils for Knee Pain Relief
Essential oils like peppermint, eucalyptus, and lavender can be massaged into the knee joint to provide relief. These oils work by reducing inflammation, improving circulation, and relaxing the muscles around the knee. Mixing a few drops of essential oil with a carrier oil like coconut or olive oil and massaging it onto the knee can offer soothing relief.
5. Hot and Cold Therapy
Alternating between hot and cold therapy can be highly effective in reducing knee pain. Cold therapy (using ice packs) helps to reduce inflammation and numb the area, while heat therapy (using a warm towel or heating pad) can relax and soothe stiff joints and muscles. This combination can be particularly effective after exercise or a long day on your feet.
6. Dietary Changes and Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Diet plays a significant role in managing knee pain and supporting joint health. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and making certain dietary changes can help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve overall joint function. Let’s delve into how specific dietary adjustments can benefit those dealing with knee pain and which foods are most effective in combating inflammation.
The Link Between Diet and Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response by the body to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can contribute to conditions like arthritis and exacerbate knee pain. Certain dietary choices can either promote or reduce inflammation in the body. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding those that trigger inflammation, you can help manage knee pain more effectively.
Key Dietary Changes for Managing Knee Pain
A) Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce joint pain and stiffness by lowering inflammation in the body. Foods rich in omega-3s include:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are excellent sources.
- Chia Seeds: A plant-based source of omega-3s.
- Flaxseeds: Ground flaxseeds are a versatile addition to various dishes.
- Walnuts: A convenient and nutritious snack.
B) Consume Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, which can contribute to inflammation and joint damage. Include the following antioxidant-rich foods in your diet:
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard contain powerful antioxidants.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower are beneficial.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds provide antioxidants.
C) Incorporate Whole Grains
Whole grains have anti-inflammatory properties and provide essential nutrients and fiber. Opt for whole grains over refined grains to help manage inflammation:
- Brown Rice: A healthy alternative to white rice.
- Quinoa: A high-protein, whole grain option.
- Oats: Rich in fiber and beneficial for heart health.
- Barley: Contains antioxidants and fiber.
D) Add Spices with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Certain spices have been shown to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Incorporate these spices into your meals:
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a compound with strong anti-inflammatory effects.
- Ginger: Has natural anti-inflammatory properties and can soothe the digestive system.
- Cinnamon: Adds flavor and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
E) Reduce Intake of Processed Foods and Sugars
Processed foods and added sugars can promote inflammation and contribute to weight gain, which can put additional stress on your knees. Limit the following:
- Sugary Snacks and Beverages: Avoid sodas, candy, and pastries.
- Processed Meats: Reduce consumption of sausages, hot dogs, and other processed meats.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Cut back on white bread, pastries, and other refined grain products.
F) Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for joint health and can help maintain the lubricating fluid in your joints. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day and limit caffeinated and sugary beverages.
Sample Anti-Inflammatory Diet Plan
Breakfast
- Oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a sprinkle of flaxseeds.
- A side of green tea.
Lunch
- Grilled salmon on a bed of spinach and kale, dressed with a lemon-turmeric vinaigrette.
- A serving of quinoa.
Snack
- A handful of walnuts or almonds.
- Sliced apple with a dash of cinnamon.
Dinner
- Baked chicken breast with a side of roasted Brussels sprouts and sweet potatoes.
- Steamed broccoli.
Dessert
- A small bowl of fresh fruit salad with a sprinkle of chia seeds.
Additional Tips for Dietary Success
a) Plan Balanced Meals
Ensure each meal includes a variety of anti-inflammatory foods to get a wide range of nutrients and benefits. Aim for a balance of lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains.
b) Monitor Portion Sizes
Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. Pay attention to portion sizes and practice mindful
c) Consult a Nutritionist
If you’re unsure how to implement these dietary changes or have specific health concerns, consider consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist. They can provide personalized advice and help create a meal plan tailored to your needs.
d) Make Gradual Changes
Start by incorporating a few anti-inflammatory foods into your diet and gradually replace less healthy options. Small changes can lead to significant improvements in overall health and knee pain management.
7. Massage Therapy
Massage therapy has long been recognized as an effective method for managing joint pain. It offers a holistic approach to address discomfort by targeting both the physical and mental aspects of the condition.
How Massage Works for Joint Pain
a) Increased Blood Flow
Massage helps to improve circulation, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to the affected joints. This increased blood flow aids in the removal of waste products and reduces inflammation.
b) Reduced Muscle Tension
Tight muscles can put added pressure on joints. Massage helps to relax and loosen these muscles, relieving strain on the affected areas.
c) Pain Relief
Massage stimulates the release of endorphins, the body’s natural pain relievers. These endorphins can help to reduce pain perception and create a sense of relaxation.
d) Improved Range of Motion
By loosening tight muscles and reducing inflammation, massage can help improve flexibility and range of motion in the joints.
e) Stress Reduction
Massage promotes relaxation and reduces stress, which can contribute to chronic pain conditions.
Types of Massage For Joint Pain
A. Deep Tissue Massage
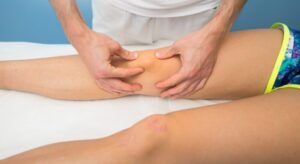
This technique focuses on releasing chronic tension in the deeper layers of muscle tissue and connective tissue, providing relief for persistent joint pain.
B. Swedish Massage

This technique is known for its relaxation benefits, Swedish massage can also help to reduce muscle tension and improve circulation, which can be beneficial for joint pain.
C. Sports Massage

This type of massage is designed to address specific muscle and joint issues, making it suitable for those with joint pain related to physical activity. It targets specific muscle groups and joints, ideal for athletes or individuals with active lifestyles.
D. Hot Stone Massage

The warmth of the stones helps to relax muscles and increase blood flow, providing soothing relief for joint discomfort.
Finally, while massage can be a valuable tool for managing joint pain, it’s important to remember that it may not provide complete relief for everyone. Combining massage with other treatments, such as exercise, physical therapy, and medication, can often provide the best results.
8. The Role of Weight Management
Excess weight can put additional pressure on your knees, exacerbating pain. Managing your weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise can relieve stress on your knee joints. Even a small amount of weight loss can make a significant difference in reducing knee pain and improving mobility.
9. Mind-Body Techniques: Yoga and Meditation
Mind-body practices like yoga and meditation can offer holistic relief from knee pain. Yoga strengthens and stretches the muscles around the knee while improving flexibility. Meditation, on the other hand, helps manage the psychological aspects of chronic pain by promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
When to See a Doctor
While home remedies can be highly effective, there are times when you should consult a doctor. If your knee pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by swelling, redness, or fever, it could indicate a more serious issue that requires medical attention. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if home remedies aren’t providing sufficient relief.

Conclusion
Knee joint pain can be a significant barrier to enjoying daily life, but it doesn’t have to be. By incorporating some of these home remedies into your routine, you can manage the pain and improve your quality of life. From the R.I.C.E method to dietary changes, these simple and natural solutions offer a way to relieve discomfort without relying solely on medications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1) Can knee pain go away on its own?
Yes, mild knee pain caused by overuse or minor injuries may resolve on its own with rest and home care. However, persistent pain should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
2) How long should I use the R.I.C.E method for knee pain?
The R.I.C.E method is most effective within the first 48 hours after an injury, but you can continue to use it as needed for pain and swelling.
3) Are there any foods that can worsen knee pain?
Yes, foods high in sugar, processed foods, and excessive red meat can contribute to inflammation and worsen knee pain.
4) Can I exercise with knee pain?
It depends on the severity and cause of the pain. Gentle exercises and stretches can be beneficial, but it’s important to avoid activities that exacerbate the pain.
5) When should I consider surgery for knee pain?
Surgery may be considered if conservative treatments, including home remedies and physical therapy, fail to provide relief, and if the pain significantly impacts your quality of life.



